The News 04/12/2025
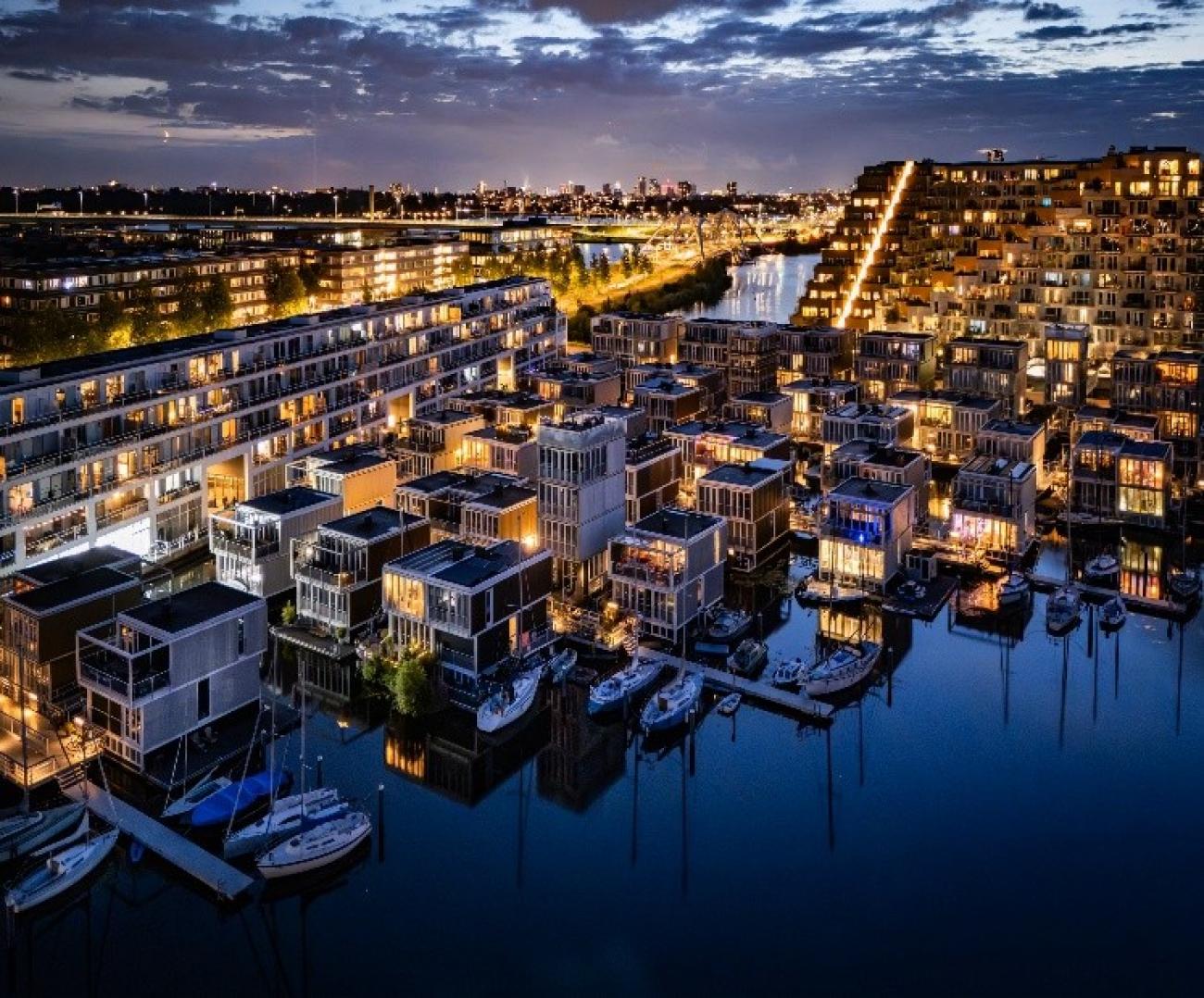
Floating Houses Amsterdam – Dutch Floating Houses Against Climate Change
The Netherlands is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change, with about a third of its area lying below sea level and the rest regularly at risk of flooding. As sea levels are forecast to continue to rise and extreme rains increase, the government is not only strengthening dikes and tidal culverts, but also testing new adaptation models. Floating housing in Amsterdam – typically the Waterbuurt and Schoonschip districts – is seen as "urban laboratories" for a new way of living: not only fighting floods, but actively living with water. In parallel with climate pressures, Amsterdam faces a shortage of housing and scarce land funds. The expansion of the city to the water helps solve two problems at the same time: increasing the supply of housing without encroaching on more land, and at the same time testing an urban model that is able to adapt to flooding and sea level rise.