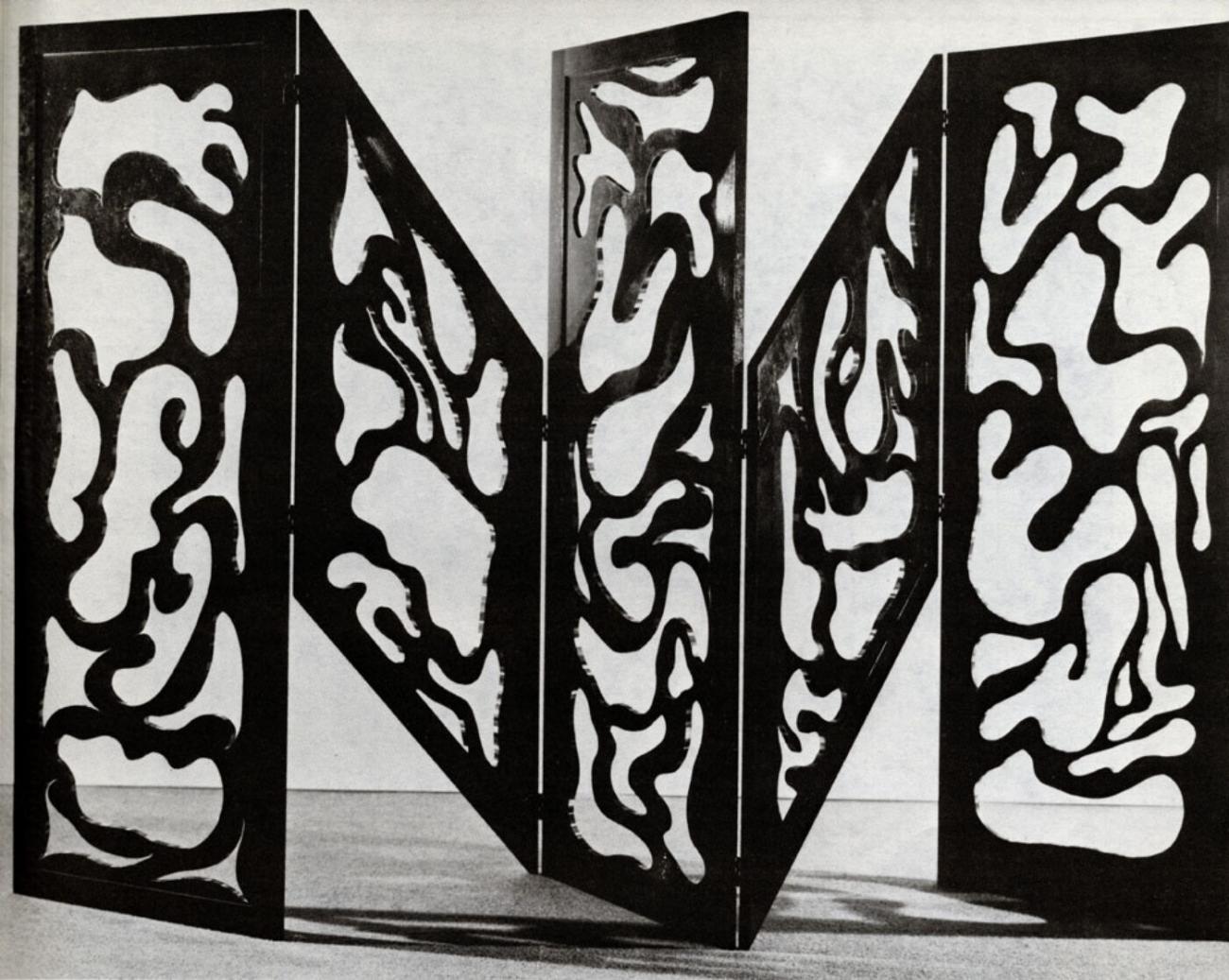
The Origin of the Screen Partition
|
The screen partition originated in ancient China during the Western Zhou Dynasty (1046–771 BCE). Initially crafted for royal palaces and noble households, it served to block drafts, divide spaces, and enhance privacy. These early screens were often adorned with intricate paintings or calligraphy, symbolizing wealth and status. |
 |
As time passed, screen partitions became a staple in traditional Asian homes, spreading to countries like Japan and Korea, where they evolved in design and functionality.
Design and Features
Traditional screen partitions are made from materials like wood, silk, paper, and bamboo. They are either fixed or foldable, with panels connected by hinges. The surface is typically decorated with:
Practical and Symbolic Uses
1. Space Division
In traditional homes, screens divide large rooms into functional sections without the permanence of walls.

2. Decorative Element
Screens add beauty and sophistication to interiors. Their designs often reflect cultural values, artistic trends, or the homeowner's status.
 |
 |
3. Feng Shui Applications
In Feng Shui, screen partitions are used to direct energy flow, block negative energy, and enhance harmony within a space.

4. Privacy and Protection
Historically, screens provided a barrier between public and private spaces, especially for women in traditional households.
Cultural Significance
Over time, the screen partition became more than just furniture; it became a cultural artifact embodying the artistic and philosophical ideals of different dynasties. For example:
Modern Applications
Today, screen partitions are experiencing a revival in interior design worldwide. They are prized for their ability to add an artistic flair to modern homes and offices, offering both functionality and beauty. Screens can now be seen in a variety of styles, blending traditional craftsmanship with contemporary aesthetics.
Conclusion
The screen partition is a timeless piece of art and utility, bridging history, culture, and modern design. Whether you’re a fan of traditional Asian decor or seeking an elegant way to divide space, a Ping Feng can be the perfect addition to your interior.
Sources: VNbuilding.vn

The News 25/12/2025
Walking by Ba Son at night and seeing the sky like "turning on the screen"? It is highly likely that you have just met Saigon Marina International Financial Centre (Saigon Marina IFC) – a 55-storey tower at No. 2 Ton Duc Thang (District 1). The façade LED system makes the building look like a giant "LED Matrix": standing far away, you feel like the whole tower is broadcasting content, constantly changing scenes according to the script.

The News 14/12/2025
Architectural Digest gợi ý Cloud Dancer phù hợp với plush fabrics và những hình khối “mềm”, tránh cảm giác cứng/rigid; họ liên hệ nó với cảm giác “weightless fullness” (nhẹ nhưng đầy) [3]. Đây là cơ hội cho các dòng vải bọc, rèm, thảm, bedding: màu trắng ngà làm nổi sợi dệt và tạo cảm giác chạm “ấm”.Pantone has announced the PANTONE 11-4201 Cloud Dancer as the Color of the Year 2026: a "buoyant" and balanced white, described as a whisper of peace in the midst of a noisy world. This is also the first time Pantone has chosen a white color since the "Color of the Year" program began in 1999. Pantone calls Cloud Dancer a "lofty/billowy" white tone that has a relaxing feel, giving the mind more space to create and innovate [1].

The News 04/12/2025
The Netherlands is one of the most vulnerable countries to climate change, with about a third of its area lying below sea level and the rest regularly at risk of flooding. As sea levels are forecast to continue to rise and extreme rains increase, the government is not only strengthening dikes and tidal culverts, but also testing new adaptation models. Floating housing in Amsterdam – typically the Waterbuurt and Schoonschip districts – is seen as "urban laboratories" for a new way of living: not only fighting floods, but actively living with water. In parallel with climate pressures, Amsterdam faces a shortage of housing and scarce land funds. The expansion of the city to the water helps solve two problems at the same time: increasing the supply of housing without encroaching on more land, and at the same time testing an urban model that is able to adapt to flooding and sea level rise.

The News 20/11/2025
Kampung Admiralty - the project that won the "Building of the Year 2018" award at the World Architecture Festival - is a clear demonstration of smart tropical green architecture. With a three-storey "club sandwich" design, a natural ventilation system that saves 13% of cooling energy, and a 125% greening rate, this project opens up many valuable lessons for Vietnamese urban projects in the context of climate change.

The News 10/11/2025
In the midst of the hustle and bustle of urban life, many Vietnamese families are looking for a different living space – where they can enjoy modernity without being far from nature. Tropical Modern villa architecture is the perfect answer to this need. Not only an aesthetic trend, this is also a smart design philosophy, harmoniously combining technology, local materials and Vietnam's typical tropical climate.

The News 25/10/2025
Hemp-lime (hempcrete) is a non-load-bearing covering material consisting of a hemp wood core (hemp shiv/hurd) combined with a lime-based adhesive, outstanding for its insulation – moisture conditioning – indoor environmental durability; in particular, IRC 2024 – Appendix BL has established a normative line applicable to low-rise housing, strengthening the technical-legal feasibility of this biomaterial.